Building a working computer from scratch may seem like rocket science to newbies, but to the computer geeks, gamers, and others that need high-powered machines to do their jobs and pursue their hobbies, it is more akin to building something out of Lego blocks. To explain the difference between NVMe, M.2 and SATA 3, we must first explain what SSD is, as its understanding is fundamental in this comparison.
SSD
SSD stands for a solid-state drive. It is essentially a device for storing data. In terms of the hierarchy of computer storage, they are just below HDDs, or hard disk drives. However, they are faster than HDDs, have lower latency and they typically use flash memory for storing data. They can use the HDD interface but have their own way of transferring and storing data that is more efficient.
They came along as the answer to a problem HDD has. HDD has moving parts and the faster it spins the disk inside it the faster you can read the data. However, there are physical limitations to this mechanism. HDDs are more mechanical and are cheaper.
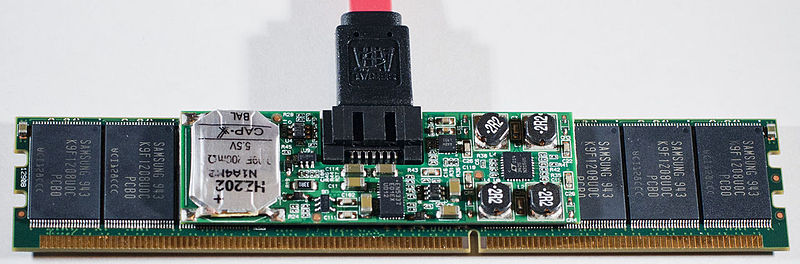
SATA 3
Serial ATA, also known as Serial Advanced Technology Attachment or SATA, is a bus interface that connects to storage devices. SATA 3 is used by the modern motherboards, allowing data to be read at 6Gb/s. Basically, it is a cable connecting the motherboard to the storage device to transfer data. SATA was the standard when SSDs first appeared on the market, as they could read data much faster than what was available on the SSDs at the time.
M.2
M.2 is a form factor of SSDs. What does that mean? Think of a laptop or a tablet. You can’t very well fill them with clunky hard disks, can you? M.2 is an SSD that is about as small as a larger packet of gum. It is smaller than the hard drives and the 2.5 inch SSD, making it perfect for these devices, as it takes up less room. In other words, you get a lot of data space without overheating. M.2, depending on the version, can support both SATA 3 and NVMe protocols for transferring data.
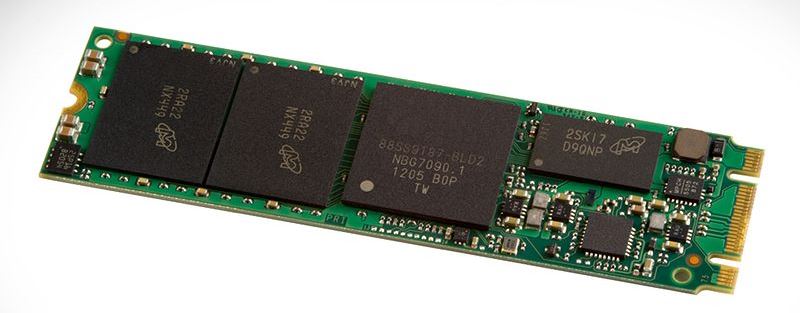
NVMe
NVMe stands for Non-Volatile Memory Express. It uses PCI Express, or Peripheral Component Interconnect Express, as a serial bus standard in order to allow you to read and process data at incredible speeds. It is, on average, 7 times faster than SATA 3. They were implemented to allow the modern SSD to process and transfer data to the fullest of their capability. Though, you are not going to need it if you are in the market for a simple computer, or even a hard-core gaming rig. It is designed for large companies that have loads of data to go through in a limited amount of time. For the computer of the regular people, SATA 3 works just fine.